A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket lifted off from Cape Canaveral, Florida Monday morning carrying a NASA probe designed to explore Jupiter’s icy moon Europa and search for signs of alien life.
With the Europa Clipper now on its 1.8-billion mile, five-and-a-half-year journey to the solar system’s largest planet, NASA has officially retired a “tremendous amount of risk on the mission,” according to Jordan Evans, Europa Clipper project manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab.
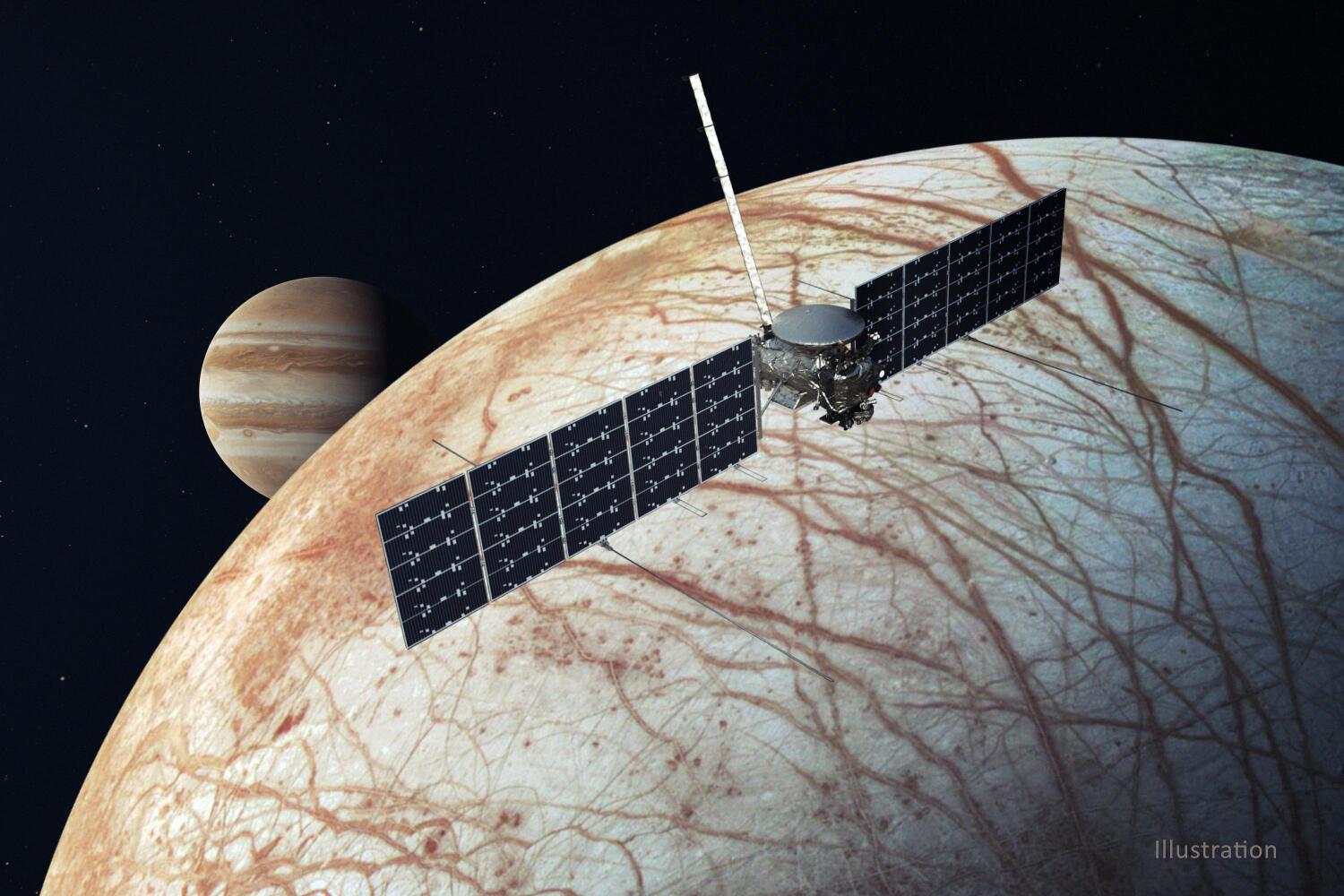
Clipper’s journey will not be direct. It will get a gravity assist by sling-shotting around Mars early next year, then boomerang back around Earth in late 2026 before zooming toward the gas giant and its icy, dynamic moon. It is scheduled to arrive in 2030 and gather data for more than four years.
When the mission ends, Clipper will fly itself into one of Jupiter’s rocky moons to ensure the spacecraft doesn’t contaminate Europa.
The launch was initially scheduled for Oct. 10, but Clipper spent that day secured in SpaceX’s hangar to ride out Hurricane Milton. The skies over Florida’s space coast were clear with few wispy clouds on Monday morning.
Scientists have advocated for a Europa mission for decades, ever since NASA’s Galileo probe found that the moon likely has a subterranean global ocean, heated by Jupiter’s gravitational forces compressing and stretching the moon’s core as it orbits the gas giant at break-neck speed.
With water, an energy source in the form of heat, and potentially organic compounds, scientists say Europa could be hospitable for alien life.
While orbiting Jupiter, Clipper will flyby Europa dozens of times and use its array of scientific instruments to study the dynamics of the moon’s subterranean ocean and look for organic compounds, a potential indicator of life.
The $5-billion Europa Clipper mission was designed and built by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in La Cañada Flintridge. It’s the largest planetary probe ever built by the space agency.
To launch the spacecraft, SpaceX employed its Falcon Heavy rocket, a variant of their Falcon 9 with an extra booster strapped to each side.
While SpaceX usually attempts to recover their boosters, this time, they let them fall into the ocean — expending all of their propellant on getting Clipper out of Earth’s gravity instead of saving some fuel to land. The fairings that protect the spacecraft as it leaves Earth will be recovered.
“The community is really fortunate to have new rockets with these heavy lift capabilities available to them,” said Matthew Shindell, planetary science and exploration curator at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum. “If you were trying to launch a mission like this a decade ago, you couldn’t do it”

